Q-learning及DQN算法
1.Q-learning 算法
核心公式:
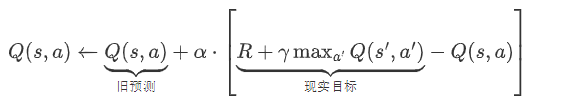
Q-learning算法是一种免模型的算法,核心思想就是基于价值,实际上就是在填一张状态-价值表,初始化都是为0,基于当前状态,计算出所有动作的reward分数,在$\epsilon$的概率下会选择随机的动作,1-$\epsilon$的概率下会选择最高分数的工作,$\epsilon$会随着学习的过程逐步衰减,这个学习过程也被称为”先探索再稳定”,实际上整个学习过程,就是在不断的去填这张状态-动作价值表,这张表相当于策略,在后面的决策动作时,会依据这张表来采取相应的动作(action).
当时Q-learning主要存在以下缺陷:
- 1、存在维度灾难问题
- 2、只能处理离散状态的决策问题,不能处理连续状态的决策问题
- 3、训练不稳定
因此,DQN的提出,用深度学习模型来近似动作价值函数的方法,解决了Q-learning维度灾难的问题、只能处理离散状态的问题,并且改善了训练的稳定性。
2.DQN算法
主要思想:

DQN主要有两个改进点:
一、经验回放机制
当产生一条新的数据时,先$ e_t = (S_t, A_t, R_t, S_{t+1}, \text{Done})$,不会立即用这条数据来进行训练,而是先把这条数据存放到Repaly Buffer中(大小为N的参数),如果存满了,则会按照先进先出的原则,丢弃掉最早进入Buffer的数据,训练时,会随机从Buffer中取出一条数据来进行训练。
解决的问题:
- 1、打破数据的时间相关性: 原本的序列数据,存在相关性,通过经验回放机制,可以打破时间相关性,学习到的规律更通用。
- 2、样本可以复用:原本可以复用,解决之前数据用一次就丢掉的问题,一条数据可能被多次抽中进行训练
- 3、提高训练稳定性
**细节:**经验回放机制在取数据的时候,会按照一定概率取随机取数据或取最大的Q值动作,这个过程是为了保证训练过程中,先进行探索再逐步稳定。
二、使用策略网络和目标网络
- 这样可以提高训练稳定性,避免Q值发散,在实际中,先更新策略网络,把目标值进行固定,达到设定的步数c时,才会将策略网络复制更新到目标网络中
解决的问题:
这样可以提高训练稳定性,避免Q值发散,在实际中,先更新策略网络,把目标值进行固定,达到设定的步数c时,才会将策略网络复制更新到目标网络中。
**为什么要这样做?**答:因为原本的目标网络和策略网路的参数存在相关性,状态的改变对两者的学习都有影响,通过先固定目标网络,可以避免单个样本造成的错误估计,避免Q值发散,使得网络训练更加稳定。
3.DQN算法实现过程
1.策略网络和目标网路的网络结构
1 | import torch.nn as nn |
2.经验回放机制实现
1 | from collections import deque # 队列 |
3.DQN智能体实现
1 | import torch |
3.训练测试函数
1 | def train(cfg, env, agent): |
4.定义环境
1 | import gym |
5.参数设置及功能函数实现
1 | import argparse |
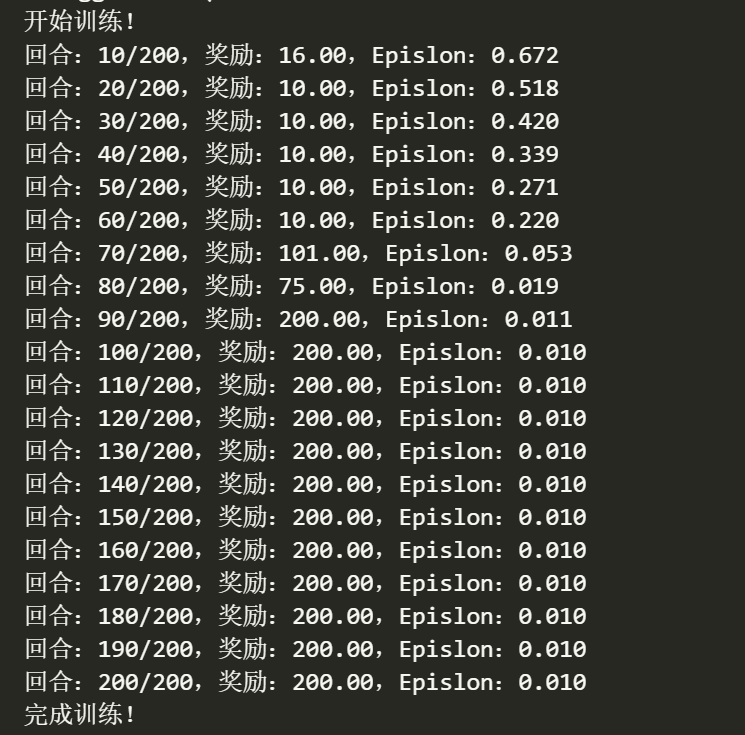
6.训练
1 | # 获取参数 |
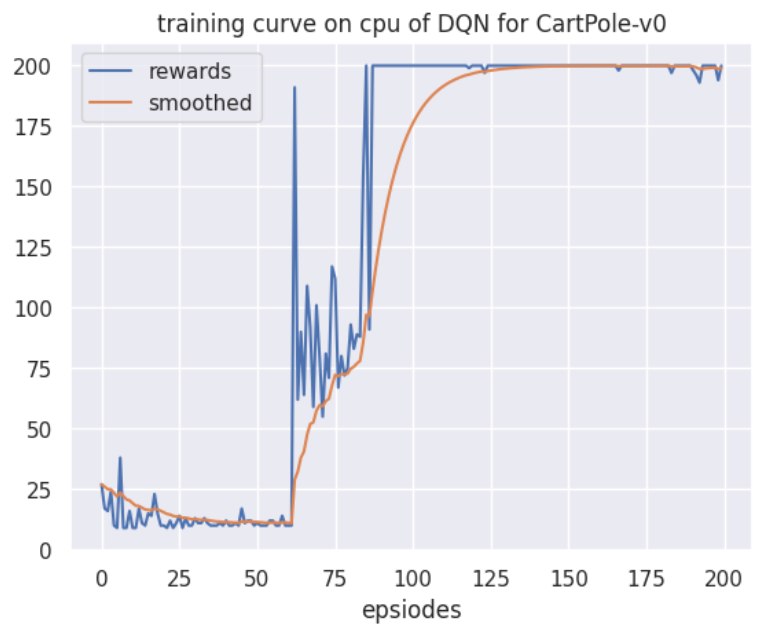
4.训练过程图